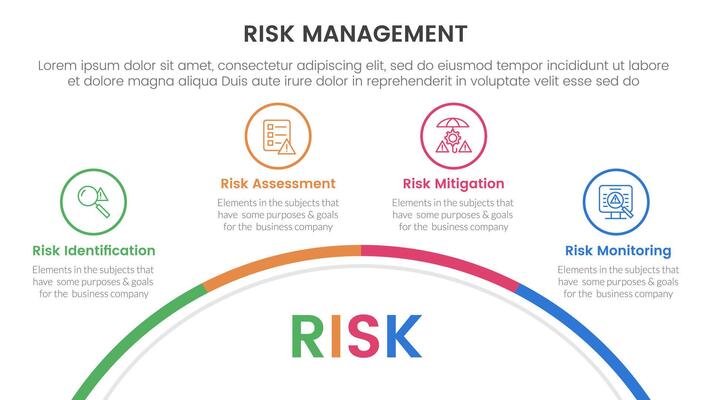
Engineering: Shaping the Future Through Innovation and Problem-Solving



- Civil Engineering: Designs and maintains infrastructure (roads, bridges, buildings).
- Mechanical Engineering: Focuses on machines, engines, and mechanical systems.
- Electrical Engineering: Deals with electrical systems, power generation, and electronics.
- Chemical Engineering: Involves chemical processes, manufacturing, and material science.
- Computer Engineering: Integrates computer science and electrical engineering to design computer systems.
- Aerospace Engineering: Designs and develops aircraft and spacecraft.
- Biomedical Engineering: Applies engineering principles to healthcare and medicine.
- Environmental Engineering: Focuses on protecting the environment and human health.
Engineering Discipline | Key Focus Areas | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
Civil Engineering | Infrastructure development and maintenance | Bridges, roads, buildings, water systems |
Mechanical Engineering | Mechanical systems, machines, and engines | Automobiles, manufacturing equipment, power plants |
Electrical Engineering | Electrical systems, electronics, and power generation | Power grids, electronic devices, communication systems |
Chemical Engineering | Chemical processes, material science, and manufacturing | Pharmaceuticals, plastics, food processing |
Computer Engineering | Computer hardware and software systems | Computers, embedded systems, network infrastructure |
Aerospace Engineering | Aircraft, spacecraft, and related technologies | Airplanes, satellites, rockets |
Biomedical Engineering | Healthcare, medical devices, and biological systems | Prosthetics, medical imaging equipment, drug delivery systems |
Environmental Engineering | Environmental protection and sustainable practices | Water treatment, air pollution control, waste management |
Engineering Discipline | Key Focus Areas | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
Civil Engineering | Infrastructure development and maintenance | Bridges, roads, buildings, water systems |
Mechanical Engineering | Mechanical systems, machines, and engines | Automobiles, manufacturing equipment, power plants |
Electrical Engineering | Electrical systems, electronics, and power generation | Power grids, electronic devices, communication systems |
Chemical Engineering | Chemical processes, material science, and manufacturing | Pharmaceuticals, plastics, food processing |
Computer Engineering | Computer hardware and software systems | Computers, embedded systems, network infrastructure |
Aerospace Engineering | Aircraft, spacecraft, and related technologies | Airplanes, satellites, rockets |
Biomedical Engineering | Healthcare, medical devices, and biological systems | Prosthetics, medical imaging equipment, drug delivery systems |
Environmental Engineering | Environmental protection and sustainable practices | Water treatment, air pollution control, waste management |

- Define the Problem: Clearly identify the need or challenge to be addressed.
- Brainstorm Solutions: Generate a wide range of potential solutions through creative thinking.
- Design and Prototype: Develop a detailed design and create a physical or virtual prototype.
- Test and Evaluate: Assess the prototype's performance and identify areas for improvement.
- Refine the Design: Modify and improve the design based on testing and evaluation results.
- Implement the Solution: Deploy the final design and monitor its performance.
Stage | Description | Activities |
|---|---|---|
Define the Problem | Clearly identify the need or challenge. | Conduct research, gather data, define constraints |
Brainstorm Solutions | Generate potential solutions. | Ideation, brainstorming sessions, exploring different approaches |
Design and Prototype | Develop a detailed design and create a prototype. | CAD modeling, simulation, building physical prototypes |
Test and Evaluate | Assess the prototype's performance. | Testing, data analysis, identifying areas for improvement |
Refine the Design | Modify and improve the design. | Iterative design changes, optimization, addressing feedback |
Implement the Solution | Deploy the final design. | Manufacturing, construction, deployment, monitoring |
Stage | Description | Activities |
|---|---|---|
Define the Problem | Clearly identify the need or challenge. | Conduct research, gather data, define constraints |
Brainstorm Solutions | Generate potential solutions. | Ideation, brainstorming sessions, exploring different approaches |
Design and Prototype | Develop a detailed design and create a prototype. | CAD modeling, simulation, building physical prototypes |
Test and Evaluate | Assess the prototype's performance. | Testing, data analysis, identifying areas for improvement |
Refine the Design | Modify and improve the design. | Iterative design changes, optimization, addressing feedback |
Implement the Solution | Deploy the final design. | Manufacturing, construction, deployment, monitoring |

- Infrastructure Development: Building and maintaining roads, bridges, and transportation systems.
- Technological Advancement: Developing new technologies and innovations in various fields.
- Healthcare Solutions: Designing medical devices and improving healthcare systems.
- Environmental Protection: Creating sustainable solutions for environmental challenges.
- Economic Growth: Contributing to economic development through innovation and infrastructure.
- Improved Quality of Life: Enhancing the quality of life through technological advancements.
Area | Engineering Contribution | Societal Impact |
|---|---|---|
Transportation | Development of efficient transportation systems | Improved mobility, reduced travel time, economic growth |
Healthcare | Design of medical devices and improved healthcare systems | Enhanced patient care, increased life expectancy, better quality of life |
Communication | Development of communication technologies | Global connectivity, instant communication, access to information |
Energy | Development of sustainable energy solutions | Reduced reliance on fossil fuels, cleaner environment, energy security |
Environment | Development of environmental protection technologies | Reduced pollution, conservation of resources, sustainable practices |
Infrastructure | Construction and maintenance of infrastructure | Safe and reliable infrastructure, economic development, improved living standards |
Area | Engineering Contribution | Societal Impact |
|---|---|---|
Transportation | Development of efficient transportation systems | Improved mobility, reduced travel time, economic growth |
Healthcare | Design of medical devices and improved healthcare systems | Enhanced patient care, increased life expectancy, better quality of life |
Communication | Development of communication technologies | Global connectivity, instant communication, access to information |
Energy | Development of sustainable energy solutions | Reduced reliance on fossil fuels, cleaner environment, energy security |
Environment | Development of environmental protection technologies | Reduced pollution, conservation of resources, sustainable practices |
Infrastructure | Construction and maintenance of infrastructure | Safe and reliable infrastructure, economic development, improved living standards |