Navigating the Landscape of Risk: Identification, Assessment, and Mitigation


- Financial Risk: The potential for monetary loss due to market fluctuations, credit defaults, or poor investment decisions.
- Operational Risk: The risk of loss resulting from inadequate or failed internal processes, people, and systems.
- Reputational Risk: The potential for damage to a company's or individual's reputation due to negative publicity or ethical breaches.
- Compliance Risk: The risk of legal or regulatory sanctions, material financial loss, or loss to reputation an organization may suffer as a result of its failure to comply with laws, regulations, rules, related self-regulatory organization standards, and codes of conduct.
Risk Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
Market Risk | Fluctuations in market prices | Stock market crash |
Credit Risk | Borrower's failure to repay debt | Loan default |
Operational Risk | Failures in internal processes | Data breach |
Compliance Risk | Violation of regulations | Environmental fines |
Risk Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
Market Risk | Fluctuations in market prices | Stock market crash |
Credit Risk | Borrower's failure to repay debt | Loan default |
Operational Risk | Failures in internal processes | Data breach |
Compliance Risk | Violation of regulations | Environmental fines |

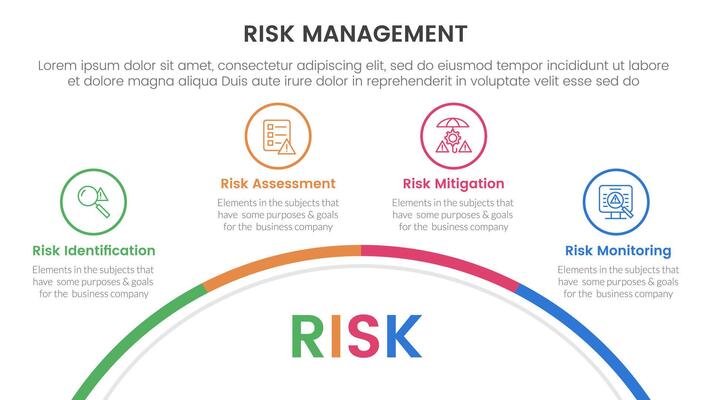
- Risk Identification: Identifying potential threats and vulnerabilities.
- Risk Assessment: Evaluating the likelihood and impact of each risk.
- Risk Prioritization: Ranking risks based on their severity and likelihood.
- Risk Mitigation: Developing and implementing strategies to reduce or eliminate risks.
- Monitoring and Review: Continuously monitoring risks and evaluating the effectiveness of mitigation strategies.
Risk Factor | Likelihood | Impact | Priority |
|---|---|---|---|
Cyber Attack | High | High | Critical |
Supply Chain Disruption | Medium | High | High |
Economic Downturn | Medium | Medium | Medium |
Employee Turnover | Low | Medium | Low |
Risk Factor | Likelihood | Impact | Priority |
|---|---|---|---|
Cyber Attack | High | High | Critical |
Supply Chain Disruption | Medium | High | High |
Economic Downturn | Medium | Medium | Medium |
Employee Turnover | Low | Medium | Low |
- Risk Avoidance: Eliminating the activity or condition that gives rise to the risk.
- Risk Transfer: Shifting the risk to a third party, typically through insurance or outsourcing.
- Risk Reduction: Implementing controls and measures to minimize the likelihood or impact of the risk.
- Risk Acceptance: Acknowledging and accepting the risk, often when the cost of mitigation outweighs the benefits.
Risk | Mitigation Strategy | Implementation |
|---|---|---|
Data Breach | Risk Reduction | Implement strong passwords, firewalls, and encryption. |
Equipment Failure | Risk Transfer | Purchase equipment insurance. |
Project Delay | Risk Reduction | Create a detailed project plan with contingency buffers. |
Natural Disaster | Risk Avoidance | Locate facilities away from high-risk zones |
Risk | Mitigation Strategy | Implementation |
|---|---|---|
Data Breach | Risk Reduction | Implement strong passwords, firewalls, and encryption. |
Equipment Failure | Risk Transfer | Purchase equipment insurance. |
Project Delay | Risk Reduction | Create a detailed project plan with contingency buffers. |
Natural Disaster | Risk Avoidance | Locate facilities away from high-risk zones |

- Financial Institutions: Managing credit risk, market risk, and operational risk.
- Healthcare Organizations: Managing patient safety, data security, and compliance risks.
- Manufacturing Companies: Managing supply chain risks, product quality risks, and safety risks.
- Technology Companies: Managing cybersecurity risks, intellectual property risks, and market competition risks.
Industry | Key Risks | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|
Banking | Credit Risk, Market Risk | Credit Scoring, Portfolio Diversification |
Healthcare | Patient Safety, Data Breach | Safety Protocols, Encryption |
Manufacturing | Supply Chain Disruption, Quality Control | Supplier Redundancy, Quality Assurance |
Technology | Cybersecurity, Intellectual Property Theft | Firewalls, Patents |
Industry | Key Risks | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|
Banking | Credit Risk, Market Risk | Credit Scoring, Portfolio Diversification |
Healthcare | Patient Safety, Data Breach | Safety Protocols, Encryption |
Manufacturing | Supply Chain Disruption, Quality Control | Supplier Redundancy, Quality Assurance |
Technology | Cybersecurity, Intellectual Property Theft | Firewalls, Patents |








